Definition Of Inquiry Letter
This letter provides a sample format for inquiring about private student aid funds. Of course, you must first identify foundations and organizations which offer such assistance well in advance of any application deadlines. You can get help finding the names and addresses of private aid sources by conducting a scholarship search on the Internet or from a reference librarian in your public library or local school. Once you have obtained contact information you will need to customize this letter to reflect your own background and needs by replacing the
bracketed boldface text below.
Sample Scholarship Inquiry Letter
[Ms. Susan B. A.Indri]
[Director of Big Money Awards]
[Lots of Money Organization]
[P.O. Box 9999]
[Moneytown, USA 99999-9999]
Dear Ms. Indri:
I am writing to inquire about any student financial assistance that the Lots of Money Organization may offer to college-bound students.
Enter a concise paragraph about your background and goals. Try to show how you meet the requirements of the organization’s financial assistance programs. If this is a letter to find out if the organization offers aid, write a short paragraph about how your background and ambitions coincide with the mission of the organization and might qualify you for assistance that may be offered.
I would greatly appreciate information about any student financial assistance available through your organization, including how I may apply for this assistance. Information about application forms and deadlines for the 2010 academic year would also be appreciated. If you require any further information, please do not hesitate to contact me by phone at 0870879200753 at the_panzel@yahoo.com.
Thank you for your consideration. I look forward to hearing from you soon.
Sincerely,
[Ms. Susan B. A.Indri]
Rabu, 27 Oktober 2010
Jumat, 15 Oktober 2010
5 Style Of Letter's Business
Business Letters
What this handout is about
This handout will help you write business letters required in many different situations, from applying for a job to requesting or delivering information. While the examples that are discussed specifically are the application letter and cover letter, this handout also highlights strategies for effective business writing in general.
Principles to keep in mind
Business writing is different
Writing for a business audience is usually quite different than writing in the humanities, social sciences, or other academic disciplines. Business writing strives to be crisp and succinct rather than evocative or creative; it stresses specificity and accuracy. This distinction does not make business writing superior or inferior to other styles. Rather, it reflects the unique purpose and considerations involved when writing in a business context.
When you write a business document, you must assume that your audience has limited time in which to read it and is likely to skim. Your readers have an interest in what you say insofar as it affects their working world. They want to know the "bottom line": the point you are making about a situation or problem and how they should respond.
Business writing varies from the conversational style often found in email messages to the more formal, legalistic style found in contracts. A style between these two extremes is appropriate for the majority of memos, emails, and letters. Writing that is too formal can alienate readers, and an attempt to be overly casual may come across as insincere or unprofessional. In business writing, as in all writing, you must know your audience.
In most cases, the business letter will be the first impression that you make on someone. Though business writing has become less formal over time, you should still take great care that your letter's content is clear and that you have proofread it carefully.
Pronouns and active versus passive voice
Personal pronouns (like I, we, and you) are important in letters and memos. In such documents, it is perfectly appropriate to refer to yourself as I and to the reader as you. Be careful, however, when you use the pronoun we in a business letter that is written on company stationery, since it commits your company to what you have written. When stating your opinion, use I; when presenting company policy, use we.
The best writers strive to achieve a style that is so clear that their messages cannot be misunderstood. One way to achieve a clear style is to minimize your use of the passive voice. Although the passive voice is sometimes necessary, often it not only makes your writing dull but also can be ambiguous or overly impersonal. Here's an example of the same point stated in passive voice and in the active voice:
PASSIVE: The net benefits of subsidiary divestiture were grossly overestimated.
[Who did the overestimating?
ACTIVE: The Global Finance Team grossly overestimated the net benefits of subsidiary divestiture.
The second version is clearer and thus preferable.
Of course, there are exceptions to every rule. What if you are the head of the Global Finance Team? You may want to get your message across without calling excessive attention to the fact that the error was your team's fault. The passive voice allows you to gloss over an unflattering point—but you should use it sparingly.
Focus and specificity
Business writing should be clear and concise. Take care, however, that your document does not turn out as an endless series of short, choppy sentences. Keep in mind also that "concise" does not have to mean "blunt"—you still need to think about your tone and the audience for whom you are writing. Consider the following examples:
After carefully reviewing this proposal, we have decided to prioritize other projects this quarter.
Nobody liked your project idea, so we are not going to give you any funding.
The first version is a weaker statement, emphasizing facts not directly relevant to its point. The second version provides the information in a simple and direct manner. But you don't need to be an expert on style to know that the first phrasing is diplomatic and respectful (even though it's less concise) as compared with the second version, which is unnecessarily harsh and likely to provoke a negative reaction.
Business letters: where to begin
Reread the description of your task (for example, the advertisement of a job opening, instructions for a proposal submission, or assignment prompt for a course). Think about your purpose and what requirements are mentioned or implied in the description of the task. List these requirements. This list can serve as an outline to govern your writing and help you stay focused, so try to make it thorough. Next, identify qualifications, attributes, objectives, or answers that match the requirements you have just listed. Strive to be exact and specific, avoiding vagueness, ambiguity, and platitudes. If there are industry- or field-specific concepts or terminology that are relevant to the task at hand, use them in a manner that will convey your competence and experience. Avoid any language that your audience may not understand. Your finished piece of writing should indicate how you meet the requirements you've listed and answer any questions raised in the description or prompt.
Application letters and cover letters
Many people believe that application letters and cover letters are essentially the same. For purposes of this handout, though, these kinds of letters are different. The letter of application is a sales letter in which you market your skills, abilities, and knowledge. A cover letter, on the other hand, is primarily a document of transmittal. It identifies an item being sent, the person to whom it is being sent, and the reason for its being sent, and provides a permanent record of the transmittal for both the writer and the reader.
Application letters
When writing an application letter, remember that you probably have competition. Your audience is a professional who screens and hires job applicants—someone who may look through dozens or even hundreds of other applications on the day she receives yours. The immediate objective of your application letter and accompanying resume is to attract this person's attention. Your ultimate goal is to obtain an interview.
As you write your application letter, be sure you complete three tasks: catch the reader's attention favorably, convince the reader that you are a qualified candidate for the job, and request an interview.
Application letter checklist:
• Identify the job by title and let the recipient know how you heard about it.
• Summarize your qualifications for the job, specifically your work experience, activities that show your leadership skills, and your educational background.
• Refer the reader to your enclosed resume.
• Ask for an interview, stating where you can be reached and when you will be available. If your prospective employer is located in another city and you plan to visit the area, mention the dates for your trip.
• If you are applying for a specific job, include any information pertinent to the position that is not included in your resume.
To save your reader time and to call attention to your strengths as a candidate, state your objective directly at the beginning of the letter.
Example: I am seeking a position as a manager in your Data Center. In such a management position, I can use my master's degree in information systems and my experience as a programmer/analyst to address business challenges in data processing.
If you have been referred to a company by one of its employees, a career counselor, a professor, or someone else, mention that before stating your job objective.
Example: During the recent ARRGH convention in Washington, D.C., one of your sales representatives, Dusty Brown, informed me of a possible opening for a manager in your Data Center. My extensive background in programming and my master's degree in information systems make me highly qualified for the position.
In subsequent paragraphs, expand on the qualifications you mentioned in your opening. Add any appropriate details, highlighting experience listed on your resume that is especially pertinent to the job you are seeking. Close with a request for an interview. Proofread your letter carefully.
Two sample letters of application are presented below. The first letter (Sample #1) is by a recent college graduate responding to a local newspaper article about the company's plan to build a new computer center. The writer is not applying for a specific job opening but describes the position he seeks. The second letter (Sample #2) is from a college senior who does not specify where she learned of the opening because she is uncertain whether a position is available.

Picture Full Block Letter Business
Legend:
1. Return Address: If your stationery has a letterhead, skip this. Otherwise, type your name, address and optionally, phone number. These days, it's common to also include an email address.
2. Date: Type the date of your letter two to six lines below the letterhead. Three are standard. If there is no letterhead, type it where shown.
3. Reference Line: If the recipient specifically requests information, such as a job reference or invoice number, type it on one or two lines, immediately below the Date (2). If you're replying to a letter, refer to it here. For example,
• Re: Job # 625-01
• Re: Your letter dated 1/1/200x.
4. Special Mailing Notations: Type in all uppercase characters, if appropriate. Examples include
• SPECIAL DELIVERY
• CERTIFIED MAIL
• AIRMAIL
5. On-Arrival Notations: Type in all uppercase characters, if appropriate. You might want to include a notation on private correspondence, such as a resignation letter. Include the same on the envelope. Examples are
• PERSONAL
• CONFIDENTIAL
6. Inside Address: Type the name and address of the person and/or company to whom you're sending the letter, three to eight lines below the last component you typed. Four lines are standard. If you type an Attention Line (7), skip the person's name here. Do the same on the envelope.
7. Attention Line: Type the name of the person to whom you're sending the letter. If you type the person's name in the Inside Address (6), skip this. Do the same on the envelope.
8. Salutation: Type the recipient's name here. Type Mr. or Ms. [Last Name] to show respect, but don't guess spelling or gender. Some common salutations are
• Ladies:
• Gentlemen:
• Dear Sir:
• Dear Sir or Madam:
• Dear [Full Name]:
• To Whom it May Concern:
9. Subject Line: Type the gist of your letter in all uppercase characters, either flush left or centered. Be concise on one line. If you type a Reference Line (3), consider if you really need this line. While it's not really necessary for most employment-related letters, examples are below.
• SUBJECT: RESIGNATION
• LETTER OF REFERENCE
• JOB INQUIRY
10. Body: Type two spaces between sentences. Keep it brief and to the point.
11. Complimentary Close: What you type here depends on the tone and degree of formality. For example,
• Respectfully yours (very formal)
• Sincerely (typical, less formal)
• Very truly yours (polite, neutral)
• Cordially yours (friendly, informal)
12. Signature Block: Leave four blank lines after the Complimentary Close (11) to sign your name. Sign your name exactly as you type it below your signature. Title is optional depending on relevancy and degree of formality. Examples are
• John Doe, Manager
• P. Smith
Director, Technical Support
• R. T. Jones - Sr. Field Engineer
13. Identification Initials: If someone typed the letter for you, he or she would typically include three of your initials in all uppercase characters, then two of his or hers in all lowercase characters. If you typed your own letter, just skip it since your name is already in the Signature Block (12). Common styles are below.
• JAD/cm
• JAD:cm
• clm
14. Enclosure Notation: This line tells the reader to look in the envelope for more. Type the singular for only one enclosure, plural for more. If you don't enclose anything, skip it. Common styles are below.
• Enclosure
• Enclosures: 3
• Enclosures (3)
15. cc: Stands for courtesy copies (formerly carbon copies). List the names of people to whom you distribute copies, in alphabetical order. If addresses would be useful to the recipient of the letter, include them. If you don't copy your letter to anyone, skip it.

Picture Block Style Letter Business

Picture Standart Letter Business

Profesional Style Letter Business
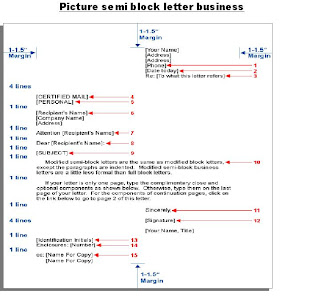
Picture semi block letter business
Legend:
1. Return Address: If your stationery has a letterhead, skip this. Otherwise, type your name, address and optionally, phone number, five spaces to the right of center or flush with the right margin. Five spaces to the right of center is common. These days, it's also common to include an email address.
2. Date: Type the date five spaces to the right of center or flush with the right margin, two to six lines below the letterhead. Five spaces to the right of center and three lines below the letterhead are common. If there is no letterhead, type it where shown.
3. Reference Line: If the recipient specifically requests information, such as a job reference or invoice number, type it on one or two lines, immediately below and aligned with the Date (2). If you're replying to a letter, refer to it here. For example,
• Re: Job # 625-01
• Re: Your letter dated 1/1/200x.
4. Special Mailing Notations: Type in all uppercase characters, if appropriate. Examples include
• SPECIAL DELIVERY
• CERTIFIED MAIL
• AIRMAIL
5. On-Arrival Notations: Type in all uppercase characters, if appropriate. You might want to include a notation on private correspondence, such as a resignation letter. Include the same on the envelope. Examples are
• PERSONAL
• CONFIDENTIAL
6. Inside Address: Type the name and address of the person and/or company to whom you're sending the letter, three to eight lines below the last component you typed. Four lines are standard. If you type an Attention Line (7), skip the person's name here. Do the same on the envelope.
7. Attention Line: Type the name of the person to whom you're sending the letter. If you type the person's name in the Inside Address (6), skip this. Do the same on the envelope.
8. Salutation: Type the recipient's name here. Type Mr. or Ms. [Last Name] to show respect, but don't guess spelling or gender. Some common salutations are
• Ladies:
• Gentlemen:
• Dear Sir:
• Dear Sir or Madam:
• Dear [Full Name]:
• To Whom it May Concern:
9. Subject Line: Type the gist of your letter in all uppercase characters. Be concise on one line. If you type a Reference Line (3), consider if you really need this line. While it's not really necessary for most employment-related letters, examples are below.
• SUBJECT: RESIGNATION
• LETTER OF REFERENCE
• JOB INQUIRY
10. Body: Indent the first sentence in paragraphs five spaces. Type two spaces between sentences. Keep it brief and to the point.
11. Complimentary Close: Type this aligned with the Date (2). What you type here depends on the tone and degree of formality. For example,
• Respectfully yours (very formal)
• Sincerely (typical, less formal)
• Very truly yours (polite, neutral)
• Cordially yours (friendly, informal)
12. Signature Block: Align this block with the Complimentary Close (11). Leave four blank lines to sign your name. Sign it exactly the same as you typed it below your signature. Title is optional depending on relevancy and degree of formality. Examples are
• John Doe, Manager
• P. Smith
Director, Technical Support
• R. T. Jones - Sr. Field Engineer
13. Identification Initials: If someone typed the letter for you, he or she would typically include three of your initials in all uppercase characters, then two of his or hers in all lowercase characters. If you typed your own letter, just skip it since your name is already in the Signature Block (12). Common styles are below.
• JAD/cm
• JAD:cm
• clm
14. Enclosure Notation: This line tells the reader to look in the envelope for more. Type the singular for only one enclosure, plural for more. If you don't enclose anything, skip it. Common styles are below.
• Enclosure
• Enclosures: 3
• Enclosures (3)
15. cc: Stands for courtesy copies (formerly carbon copies). List the names of people to whom you distribute copies, in alphabetical order. If addresses would be useful to the recipient of the letter, include them. If you don't copy your letter to anyone, skip it.
Tips:
* Replace the text in brackets [ ] with the component indicated. Don't type the brackets.
* Try to keep your letters to one page, but see page 2 of this sample if you need continuation pages.
* How many blank lines you add between lines that require more than one, depends on how much space is available on the page.
* The same goes for margins. One and one-half inch (108 points) for short letters and one inch (72 points) for longer letters are standard. If there is a letterhead, its position determines the top margin on page 1.
* If you don't type one of the more formal components, don't leave space for them. For example, if you don't type the Reference Line (3), Special Mailing Notations (4) and On-Arrival Notations (5), type the Inside Address (6) four lines below the Date (2).
What this handout is about
This handout will help you write business letters required in many different situations, from applying for a job to requesting or delivering information. While the examples that are discussed specifically are the application letter and cover letter, this handout also highlights strategies for effective business writing in general.
Principles to keep in mind
Business writing is different
Writing for a business audience is usually quite different than writing in the humanities, social sciences, or other academic disciplines. Business writing strives to be crisp and succinct rather than evocative or creative; it stresses specificity and accuracy. This distinction does not make business writing superior or inferior to other styles. Rather, it reflects the unique purpose and considerations involved when writing in a business context.
When you write a business document, you must assume that your audience has limited time in which to read it and is likely to skim. Your readers have an interest in what you say insofar as it affects their working world. They want to know the "bottom line": the point you are making about a situation or problem and how they should respond.
Business writing varies from the conversational style often found in email messages to the more formal, legalistic style found in contracts. A style between these two extremes is appropriate for the majority of memos, emails, and letters. Writing that is too formal can alienate readers, and an attempt to be overly casual may come across as insincere or unprofessional. In business writing, as in all writing, you must know your audience.
In most cases, the business letter will be the first impression that you make on someone. Though business writing has become less formal over time, you should still take great care that your letter's content is clear and that you have proofread it carefully.
Pronouns and active versus passive voice
Personal pronouns (like I, we, and you) are important in letters and memos. In such documents, it is perfectly appropriate to refer to yourself as I and to the reader as you. Be careful, however, when you use the pronoun we in a business letter that is written on company stationery, since it commits your company to what you have written. When stating your opinion, use I; when presenting company policy, use we.
The best writers strive to achieve a style that is so clear that their messages cannot be misunderstood. One way to achieve a clear style is to minimize your use of the passive voice. Although the passive voice is sometimes necessary, often it not only makes your writing dull but also can be ambiguous or overly impersonal. Here's an example of the same point stated in passive voice and in the active voice:
PASSIVE: The net benefits of subsidiary divestiture were grossly overestimated.
[Who did the overestimating?
ACTIVE: The Global Finance Team grossly overestimated the net benefits of subsidiary divestiture.
The second version is clearer and thus preferable.
Of course, there are exceptions to every rule. What if you are the head of the Global Finance Team? You may want to get your message across without calling excessive attention to the fact that the error was your team's fault. The passive voice allows you to gloss over an unflattering point—but you should use it sparingly.
Focus and specificity
Business writing should be clear and concise. Take care, however, that your document does not turn out as an endless series of short, choppy sentences. Keep in mind also that "concise" does not have to mean "blunt"—you still need to think about your tone and the audience for whom you are writing. Consider the following examples:
After carefully reviewing this proposal, we have decided to prioritize other projects this quarter.
Nobody liked your project idea, so we are not going to give you any funding.
The first version is a weaker statement, emphasizing facts not directly relevant to its point. The second version provides the information in a simple and direct manner. But you don't need to be an expert on style to know that the first phrasing is diplomatic and respectful (even though it's less concise) as compared with the second version, which is unnecessarily harsh and likely to provoke a negative reaction.
Business letters: where to begin
Reread the description of your task (for example, the advertisement of a job opening, instructions for a proposal submission, or assignment prompt for a course). Think about your purpose and what requirements are mentioned or implied in the description of the task. List these requirements. This list can serve as an outline to govern your writing and help you stay focused, so try to make it thorough. Next, identify qualifications, attributes, objectives, or answers that match the requirements you have just listed. Strive to be exact and specific, avoiding vagueness, ambiguity, and platitudes. If there are industry- or field-specific concepts or terminology that are relevant to the task at hand, use them in a manner that will convey your competence and experience. Avoid any language that your audience may not understand. Your finished piece of writing should indicate how you meet the requirements you've listed and answer any questions raised in the description or prompt.
Application letters and cover letters
Many people believe that application letters and cover letters are essentially the same. For purposes of this handout, though, these kinds of letters are different. The letter of application is a sales letter in which you market your skills, abilities, and knowledge. A cover letter, on the other hand, is primarily a document of transmittal. It identifies an item being sent, the person to whom it is being sent, and the reason for its being sent, and provides a permanent record of the transmittal for both the writer and the reader.
Application letters
When writing an application letter, remember that you probably have competition. Your audience is a professional who screens and hires job applicants—someone who may look through dozens or even hundreds of other applications on the day she receives yours. The immediate objective of your application letter and accompanying resume is to attract this person's attention. Your ultimate goal is to obtain an interview.
As you write your application letter, be sure you complete three tasks: catch the reader's attention favorably, convince the reader that you are a qualified candidate for the job, and request an interview.
Application letter checklist:
• Identify the job by title and let the recipient know how you heard about it.
• Summarize your qualifications for the job, specifically your work experience, activities that show your leadership skills, and your educational background.
• Refer the reader to your enclosed resume.
• Ask for an interview, stating where you can be reached and when you will be available. If your prospective employer is located in another city and you plan to visit the area, mention the dates for your trip.
• If you are applying for a specific job, include any information pertinent to the position that is not included in your resume.
To save your reader time and to call attention to your strengths as a candidate, state your objective directly at the beginning of the letter.
Example: I am seeking a position as a manager in your Data Center. In such a management position, I can use my master's degree in information systems and my experience as a programmer/analyst to address business challenges in data processing.
If you have been referred to a company by one of its employees, a career counselor, a professor, or someone else, mention that before stating your job objective.
Example: During the recent ARRGH convention in Washington, D.C., one of your sales representatives, Dusty Brown, informed me of a possible opening for a manager in your Data Center. My extensive background in programming and my master's degree in information systems make me highly qualified for the position.
In subsequent paragraphs, expand on the qualifications you mentioned in your opening. Add any appropriate details, highlighting experience listed on your resume that is especially pertinent to the job you are seeking. Close with a request for an interview. Proofread your letter carefully.
Two sample letters of application are presented below. The first letter (Sample #1) is by a recent college graduate responding to a local newspaper article about the company's plan to build a new computer center. The writer is not applying for a specific job opening but describes the position he seeks. The second letter (Sample #2) is from a college senior who does not specify where she learned of the opening because she is uncertain whether a position is available.

Picture Full Block Letter Business
Legend:
1. Return Address: If your stationery has a letterhead, skip this. Otherwise, type your name, address and optionally, phone number. These days, it's common to also include an email address.
2. Date: Type the date of your letter two to six lines below the letterhead. Three are standard. If there is no letterhead, type it where shown.
3. Reference Line: If the recipient specifically requests information, such as a job reference or invoice number, type it on one or two lines, immediately below the Date (2). If you're replying to a letter, refer to it here. For example,
• Re: Job # 625-01
• Re: Your letter dated 1/1/200x.
4. Special Mailing Notations: Type in all uppercase characters, if appropriate. Examples include
• SPECIAL DELIVERY
• CERTIFIED MAIL
• AIRMAIL
5. On-Arrival Notations: Type in all uppercase characters, if appropriate. You might want to include a notation on private correspondence, such as a resignation letter. Include the same on the envelope. Examples are
• PERSONAL
• CONFIDENTIAL
6. Inside Address: Type the name and address of the person and/or company to whom you're sending the letter, three to eight lines below the last component you typed. Four lines are standard. If you type an Attention Line (7), skip the person's name here. Do the same on the envelope.
7. Attention Line: Type the name of the person to whom you're sending the letter. If you type the person's name in the Inside Address (6), skip this. Do the same on the envelope.
8. Salutation: Type the recipient's name here. Type Mr. or Ms. [Last Name] to show respect, but don't guess spelling or gender. Some common salutations are
• Ladies:
• Gentlemen:
• Dear Sir:
• Dear Sir or Madam:
• Dear [Full Name]:
• To Whom it May Concern:
9. Subject Line: Type the gist of your letter in all uppercase characters, either flush left or centered. Be concise on one line. If you type a Reference Line (3), consider if you really need this line. While it's not really necessary for most employment-related letters, examples are below.
• SUBJECT: RESIGNATION
• LETTER OF REFERENCE
• JOB INQUIRY
10. Body: Type two spaces between sentences. Keep it brief and to the point.
11. Complimentary Close: What you type here depends on the tone and degree of formality. For example,
• Respectfully yours (very formal)
• Sincerely (typical, less formal)
• Very truly yours (polite, neutral)
• Cordially yours (friendly, informal)
12. Signature Block: Leave four blank lines after the Complimentary Close (11) to sign your name. Sign your name exactly as you type it below your signature. Title is optional depending on relevancy and degree of formality. Examples are
• John Doe, Manager
• P. Smith
Director, Technical Support
• R. T. Jones - Sr. Field Engineer
13. Identification Initials: If someone typed the letter for you, he or she would typically include three of your initials in all uppercase characters, then two of his or hers in all lowercase characters. If you typed your own letter, just skip it since your name is already in the Signature Block (12). Common styles are below.
• JAD/cm
• JAD:cm
• clm
14. Enclosure Notation: This line tells the reader to look in the envelope for more. Type the singular for only one enclosure, plural for more. If you don't enclose anything, skip it. Common styles are below.
• Enclosure
• Enclosures: 3
• Enclosures (3)
15. cc: Stands for courtesy copies (formerly carbon copies). List the names of people to whom you distribute copies, in alphabetical order. If addresses would be useful to the recipient of the letter, include them. If you don't copy your letter to anyone, skip it.

Picture Block Style Letter Business

Picture Standart Letter Business

Profesional Style Letter Business

Picture semi block letter business
Legend:
1. Return Address: If your stationery has a letterhead, skip this. Otherwise, type your name, address and optionally, phone number, five spaces to the right of center or flush with the right margin. Five spaces to the right of center is common. These days, it's also common to include an email address.
2. Date: Type the date five spaces to the right of center or flush with the right margin, two to six lines below the letterhead. Five spaces to the right of center and three lines below the letterhead are common. If there is no letterhead, type it where shown.
3. Reference Line: If the recipient specifically requests information, such as a job reference or invoice number, type it on one or two lines, immediately below and aligned with the Date (2). If you're replying to a letter, refer to it here. For example,
• Re: Job # 625-01
• Re: Your letter dated 1/1/200x.
4. Special Mailing Notations: Type in all uppercase characters, if appropriate. Examples include
• SPECIAL DELIVERY
• CERTIFIED MAIL
• AIRMAIL
5. On-Arrival Notations: Type in all uppercase characters, if appropriate. You might want to include a notation on private correspondence, such as a resignation letter. Include the same on the envelope. Examples are
• PERSONAL
• CONFIDENTIAL
6. Inside Address: Type the name and address of the person and/or company to whom you're sending the letter, three to eight lines below the last component you typed. Four lines are standard. If you type an Attention Line (7), skip the person's name here. Do the same on the envelope.
7. Attention Line: Type the name of the person to whom you're sending the letter. If you type the person's name in the Inside Address (6), skip this. Do the same on the envelope.
8. Salutation: Type the recipient's name here. Type Mr. or Ms. [Last Name] to show respect, but don't guess spelling or gender. Some common salutations are
• Ladies:
• Gentlemen:
• Dear Sir:
• Dear Sir or Madam:
• Dear [Full Name]:
• To Whom it May Concern:
9. Subject Line: Type the gist of your letter in all uppercase characters. Be concise on one line. If you type a Reference Line (3), consider if you really need this line. While it's not really necessary for most employment-related letters, examples are below.
• SUBJECT: RESIGNATION
• LETTER OF REFERENCE
• JOB INQUIRY
10. Body: Indent the first sentence in paragraphs five spaces. Type two spaces between sentences. Keep it brief and to the point.
11. Complimentary Close: Type this aligned with the Date (2). What you type here depends on the tone and degree of formality. For example,
• Respectfully yours (very formal)
• Sincerely (typical, less formal)
• Very truly yours (polite, neutral)
• Cordially yours (friendly, informal)
12. Signature Block: Align this block with the Complimentary Close (11). Leave four blank lines to sign your name. Sign it exactly the same as you typed it below your signature. Title is optional depending on relevancy and degree of formality. Examples are
• John Doe, Manager
• P. Smith
Director, Technical Support
• R. T. Jones - Sr. Field Engineer
13. Identification Initials: If someone typed the letter for you, he or she would typically include three of your initials in all uppercase characters, then two of his or hers in all lowercase characters. If you typed your own letter, just skip it since your name is already in the Signature Block (12). Common styles are below.
• JAD/cm
• JAD:cm
• clm
14. Enclosure Notation: This line tells the reader to look in the envelope for more. Type the singular for only one enclosure, plural for more. If you don't enclose anything, skip it. Common styles are below.
• Enclosure
• Enclosures: 3
• Enclosures (3)
15. cc: Stands for courtesy copies (formerly carbon copies). List the names of people to whom you distribute copies, in alphabetical order. If addresses would be useful to the recipient of the letter, include them. If you don't copy your letter to anyone, skip it.
Tips:
* Replace the text in brackets [ ] with the component indicated. Don't type the brackets.
* Try to keep your letters to one page, but see page 2 of this sample if you need continuation pages.
* How many blank lines you add between lines that require more than one, depends on how much space is available on the page.
* The same goes for margins. One and one-half inch (108 points) for short letters and one inch (72 points) for longer letters are standard. If there is a letterhead, its position determines the top margin on page 1.
* If you don't type one of the more formal components, don't leave space for them. For example, if you don't type the Reference Line (3), Special Mailing Notations (4) and On-Arrival Notations (5), type the Inside Address (6) four lines below the Date (2).
Langganan:
Komentar (Atom)